Introduction
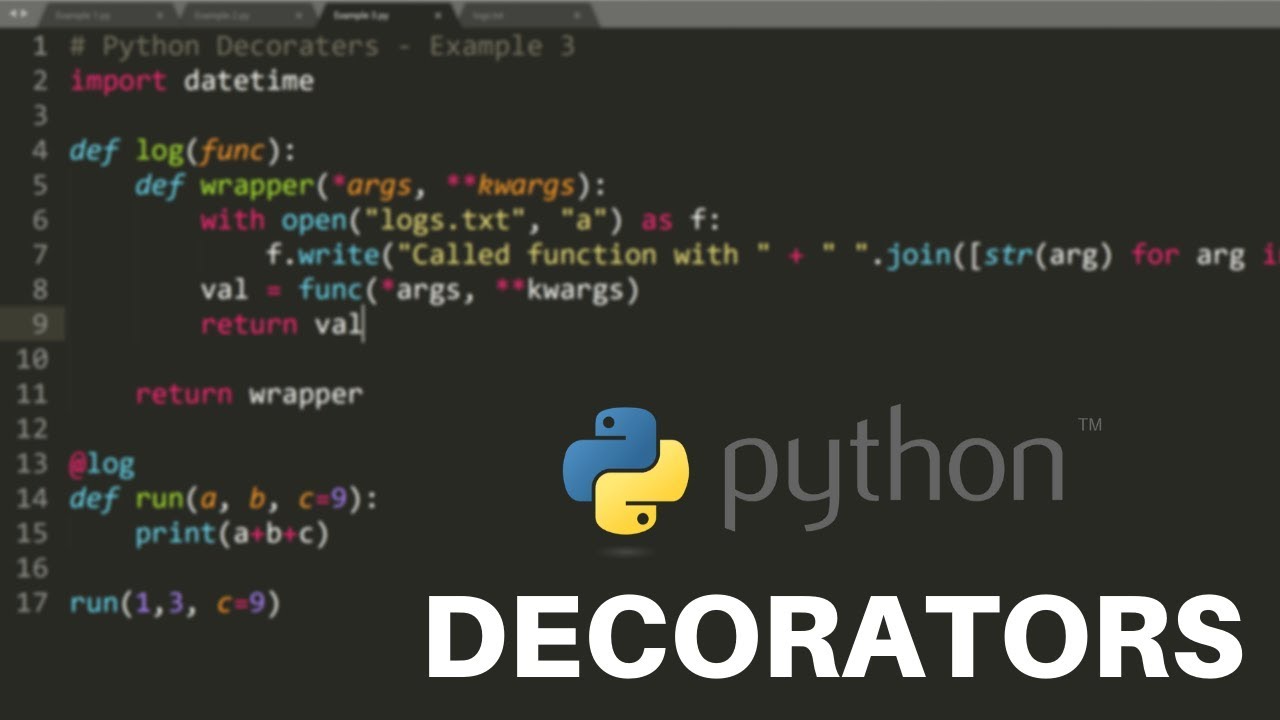
Decorators are a powerful feature in Python that allow you to modify the behavior of functions or classes. They are used for logging, access control, memoization, and more. This blog post will introduce you to Python decorators, providing examples to help you understand their usage.
What are Decorators?
A decorator is a function that wraps another function or class, modifying its behavior. Decorators are denoted by the @ symbol followed by the decorator function name, placed above the function or class definition.
Basic Decorator Example
Here's a simple decorator that prints a message before and after a function call:

Output:

Decorators with Arguments
Decorators can also accept arguments by nesting another function:

Output:

Using functools.wraps
To preserve the original function's metadata (such as name, docstring), use functools.wraps in your decorators:

Output:

Class Decorators
Decorators can also be applied to classes. Here's an example of a class decorator:

Output:

