Introduction
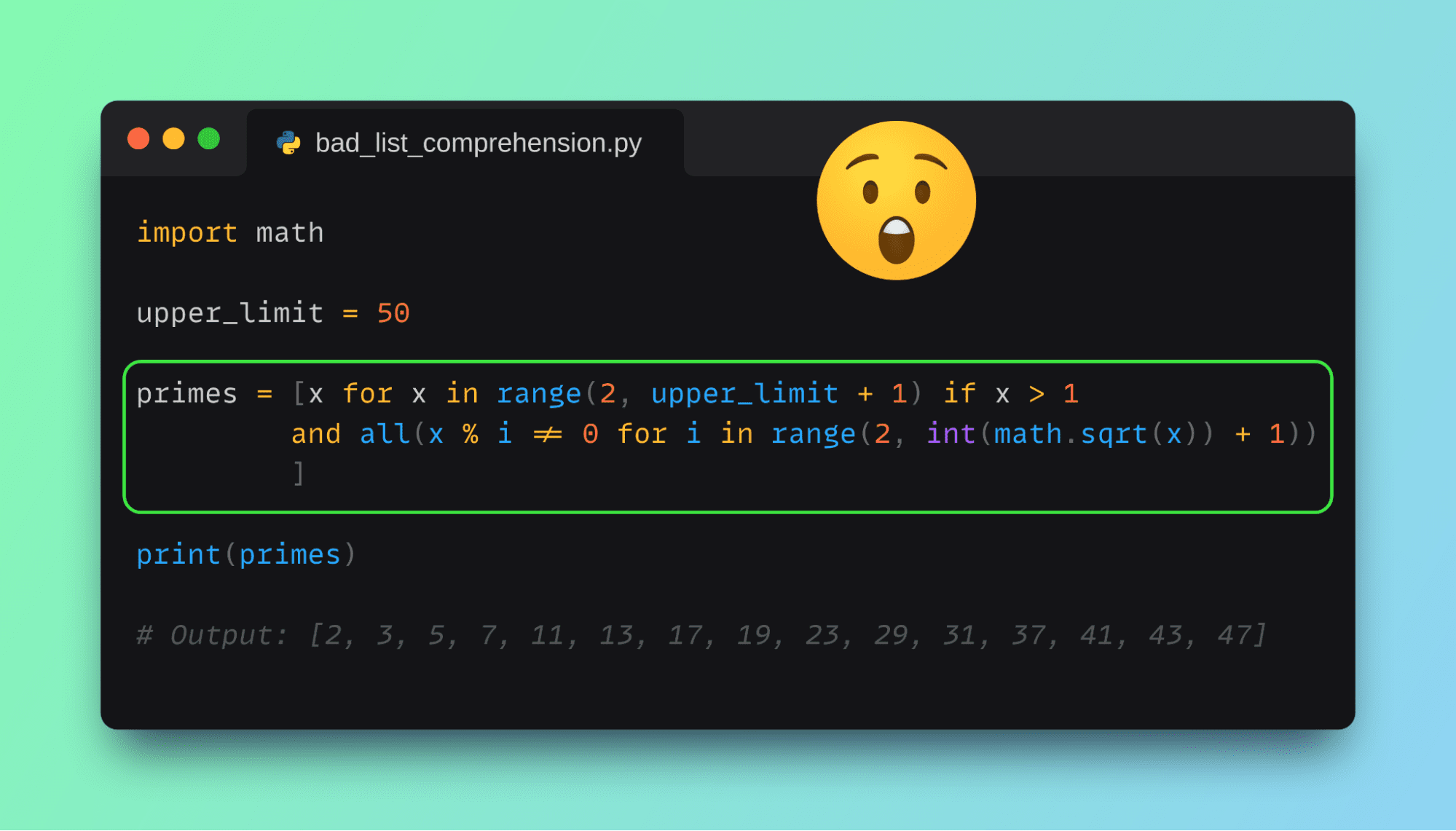
In Python, we often write loops to create lists, but what if I told you there’s a more elegant way to do this? Enter list comprehensions—a concise and expressive method for generating lists in Python. They might seem a bit daunting at first, but once you get the hang of them, you’ll find yourself using them everywhere.
What is a List Comprehension?
List comprehensions provide a syntactically compact way to generate lists. Instead of writing multiple lines of code with a for loop, you can accomplish the same task in just one line.
Syntax Breakdown
The basic syntax of a list comprehension is:

Expression: This is the value or operation to be applied to each item.
Iterable: The collection of items you’re looping through.
Condition (optional): A filter to include only items that meet a certain criterion.
Examples in Action
Basic Example:

- This creates a list of squares:
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25].
- This creates a list of squares:
With a Condition:

This filters out the odd numbers, leaving
[2, 4].
When to Use List Comprehensions
List comprehensions are great when you want to transform or filter a list in a single readable line. However, avoid using them for complex operations as it can make your code harder to read.
